A Deep Dive into Personalized Medicine for Rare Diseases
What if the key to managing a rare disease wasn’t a single cure for everyone, but a unique map created just for you? For so many families in our community, the journey has been a "diagnostic odyssey," a long, isolating search for answers.
Today, we’re exploring how personalized medicine is finally helping us draw that map, one person at a time. We'll walk with you through this incredible new chapter of hope.
I. The Shared Challenge of Rare Diseases
A rare disease is a condition that affects a small number of people. However, when viewed together, their impact is immense. In fact, over 6,000 rare diseases affect one in ten people worldwide. This means the total number of people is massive, despite each condition's individual rarity. Many of these conditions are serious, chronic, and progressive.
For too long, patients have faced huge hurdles. The search for an accurate diagnosis can take years. This long wait creates significant emotional and financial strain. Once a diagnosis is found, another challenge often appears. Over 95% of rare diseases have no approved, effective treatment. This lack of options can feel overwhelming. But a new approach is changing this story.
II. A New Approach: What is Personalized Medicine?
Personalized medicine is a fundamental shift in healthcare. It moves away from a "one-size-fits-all" approach to treatment. Instead, it customizes medical care for each patient. This approach considers a person’s unique genetic profile and lifestyle. It also accounts for environmental factors. The goal is to understand a condition with high resolution. This allows us to trace causes back to their root molecular origin.
This new era of medicine has been driven by amazing scientific leaps. For example, the Human Genome Project gave us a map of our genetic code. This project was a huge step forward. It deepened our understanding of how genes influence health and disease. As a result, we now have powerful tools for diagnosis and treatment.
III. Finding Clues: The Power of Advanced Diagnostics
One of the greatest benefits of personalized medicine is its diagnostic power. It can dramatically shorten the long, difficult search for answers. This is possible because of advanced diagnostic tools.
A. Peering into Our Genetic Code
Genomic analysis is a key part of personalized medicine. It uses genetic testing to find the cause of a rare disease. For instance, technologies like Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) allow for rapid DNA sequencing. This helps clinicians pinpoint genetic causes with greater speed and accuracy.
-
Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) looks at the protein-coding parts of your genes. Over 80% of disease-causing mutations are found here. So, WES is very useful for many rare genetic disorders.
-
Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) examines your entire genetic code. It provides a complete view of your genetic makeup. This is crucial for understanding more complex rare diseases.
These tools provide an incredible amount of information from a single patient. This creates "big data" even for very rare conditions. As a result, we can identify subtle patterns that were previously hidden.
B. Using Biomarkers to Guide Care
Biomarkers are another vital tool. They are measurable signs that show a biological state in the body. They can help diagnose a disease or predict its progression. They also help assess how someone might respond to a therapy.
There are several types of biomarkers used in rare disease care:
-
Genomic Biomarkers are the genetic mutations that cause a disease.
-
Transcriptomic Biomarkers measure RNA levels to monitor a therapy’s response.
-
Proteomic Biomarkers involve the study of proteins that indicate disease status.
-
Metabolomic Biomarkers reflect the real-time metabolic state of your body.
These tools work together to create a detailed "fingerprint" of a disease. This moves care beyond a simple diagnosis. It allows for a dynamic, personalized management strategy.
IV. Tailored Treatments: Innovations in Therapy
Understanding the root cause of a disease opens the door to new treatments. Personalized medicine is leading to therapies that target the specific mechanisms of a condition.
A. Precision at the Molecular Level
Targeted therapies are designed to address specific genetic mutations or protein defects. For example, a drug like Trikafta has been very successful for cystic fibrosis. It addresses the underlying cause of the disease, not just the symptoms. This is a profound change from older, more generalized treatments.
B. Correcting the Genetic Root Cause
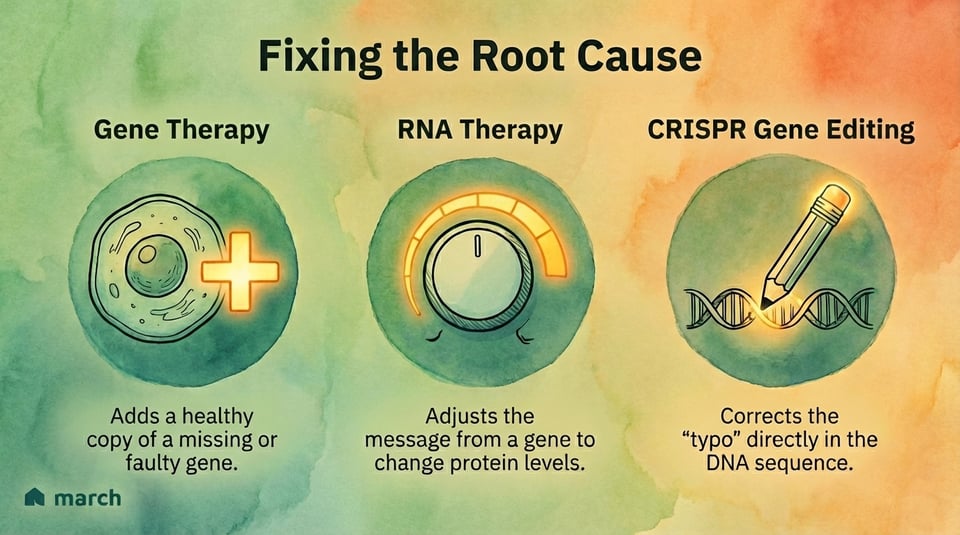
Gene and RNA-based therapies are a huge leap forward. They work by directly intervening at the genetic level.
-
Gene therapy introduces healthy copies of genes to replace faulty ones. Zolgensma, for instance, delivers a functional gene for children with Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA). This can prevent further muscle degeneration.
-
RNA-based therapies work by controlling how genes produce proteins. Spinraza for SMA is a great example. It helps the body produce a protein that is missing.
-
CRISPR gene editing is another powerful tool. It works like "molecular scissors" to precisely fix errors in DNA. This technology holds immense promise for directly correcting genetic diseases.
These therapies offer hope for conditions once considered untreatable. The real-world impact is significant. Patients receiving these treatments have experienced life-changing improvements. They have gained the ability to breathe on their own, walk, and perform daily tasks. These are monumental shifts in independence and dignity.
V. Beyond the Cure: The Importance of Supportive Care
While we celebrate these breakthroughs, we must also be realistic. Effective treatments are not yet available for every rare disease. Living with a rare condition often means managing complex needs. Therefore, comprehensive supportive care is an essential part of the journey.
This holistic approach addresses the whole person. It includes physical, emotional, social, and spiritual support.
-
Palliative care focuses on improving quality of life by managing pain and other symptoms.
-
Rehabilitation strategies like physical and occupational therapy are crucial. They help improve mobility and assist with daily activities.
-
Psychosocial support is also vital. Support groups and counseling help patients and families navigate the emotional toll of a rare disease.
Community is a powerful force for resilience and knowledge. Patient advocacy groups provide invaluable resources and a collective voice. They transform individual isolation into shared strength. This ensures that patients and families feel empowered on their journey.
VI. The Path Forward: Hope, Realism, and Our Journey Together
The road ahead is bright, but challenges remain. Funding for research can be difficult to secure. Patient access to expensive new therapies is a major hurdle. And regulatory pathways can be complex and slow.
However, there is great reason for hope. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is helping accelerate research and diagnosis. New technologies like personalized nanomedicines may soon make treatments more accessible. Most importantly, collaboration is growing stronger every day. Researchers, doctors, companies, and patient groups are working together. This teamwork is essential for turning scientific promise into real-world impact.
Personalized medicine represents a profound commitment. It is a promise that no patient, no matter how rare their condition, is left behind. We are here to support you with clear, trustworthy information. We will celebrate every step forward and be honest about the challenges. Your journey matters, and we are on this path together. You are not alone.
This journey is challenging, but you don't have to walk it alone. At March, we are a community built on shared experience, and we are here to support you as we all move forward, together.
Want a helpful overview of personalized medicine? Our podcast episode explores this important topic in detail.
Sources
-
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. The diagnostic odyssey in rare diseases: a scoping review.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7877825/ -
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Personalized medicine in rare diseases: a systematic review.
https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/11/3/887 -
mdpi.com. Personalized medicine in rare diseases: challenges and opportunities.
https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9721/8/4/42 -
clinicalleader.com. At the intersection of rare disease and precision medicine.
https://www.clinicalleader.com/doc/at-the-intersection-of-rare-disease-and-precision-medicine-a-road-to-growth-0001 -
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Defining and managing rare diseases.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8861960/ -
frontiersin.org. The public health significance of rare diseases.
https://www.orpha.net/en/other-information/about-rare-diseases -
rarediseases.org. The history of the Orphan Drug Act.
https://rarediseases.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/NORD-TimeLine.pdf -
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. The reciprocal relationship between rare diseases and precision medicine.
https://www.clinicalleader.com/doc/at-the-intersection-of-rare-disease-and-precision-medicine-a-road-to-growth-0001 -
rarediseases.org. The impact of rare diseases on patients and families.
https://rarediseases.org/ -
wolterskluwer.com. How to care for patients with very rare diseases.
https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/expert-insights/how-to-care-for-patients-with-very-rare-diseases -
frontiersin.org. Artificial intelligence in rare diseases.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6174191/ -
rarediseases.org. Underdiagnosis of rare diseases.
https://www.orpha.net/en/other-information/about-rare-diseases -
rarediseases.org. NORD timeline.
https://rarediseases.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/NORD-TimeLine.pdf -
creyos.com. Personalized medicine.
https://creyos.com/blog/personalized-medicine -
numberanalytics.com. Genomics in rare disease diagnosis.
https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/rare-disease-diagnosis-personalized-medicine -
lifearc.org. Challenges in rare disease research.
https://www.lifearc.org/2024/6-challenges-in-rare-disease-research-and-how-we-can-overcome-them/ -
numberanalytics.com. Advances in personalized medicine for rare diseases.
https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/advances-personalized-medicine-rare-diseases -
numberanalytics.com. Genomics in rare disease diagnosis and treatment.
https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/genomics-rare-disease-diagnosis-treatment -
mdpi.com. Personalized medicine and rare diseases.
https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/11/3/887 -
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. The Human Genome Project and its impact.
https://www.acc.org/Latest-in-Cardiology/Articles/2018/10/14/12/42/Harold-on-History-The-Evolution-of-Personalized-Medicine -
my.clevelandclinic.org. Rare and orphan diseases.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/rare-and-orphan-diseases -
fromtestingtotargetedtreatments.org. Accessing precision medicine.
https://www.fromtestingtotargetedtreatments.org/why-accessing-precision-medicine-can-be-an-impossible-task-for-those-with-a-rare-disease/ -
acc.org. The evolution of personalized medicine.
https://www.acc.org/Latest-in-Cardiology/Articles/2018/10/14/12/42/Harold-on-History-The-Evolution-of-Personalized-Medicine -
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. The impact of the Human Genome Project on medicine.
https://www.acc.org/Latest-in-Cardiology/Articles/2018/10/14/12/42/Harold-on-History-The-Evolution-of-Personalized-Medicine -
raregenomics.org. Funding challenges in rare disease research.
https://www.raregenomics.org/news-events-and-blogs/2025/6/3/funding-challenges-in-rare-disease-research-how-financial-support-can-transform-the-rare-disease-landscape -
rarediseases.org. National Rehabilitation Association.
https://rarediseases.org/organizations/national-rehabilitation-association/ -
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Pharmacogenomics in rare disease management.
https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/11/3/887 -
ingena.org.au. How genomics is transforming rare disease diagnosis.
https://ingena.org.au/how-genomics-is-transforming-rare-disease-diagnosis-and-treatment/









